Does Diabetes Qualify For Disability Benefits?
If you struggle with diabetes or suspect that you may have this condition, you likely already know that depending upon its severity, it can significantly affect your ability to function normally on a day-to-day basis. If the condition is severe enough, it may even be disabling to the extent that it prevents you from being able to work. That can cause significant financial difficulties and may make it difficult to continue to provide for yourself and those you love.
If you find yourself in this situation, you may wonder whether or not having diabetes may qualify you for disability benefits. It’s a reasonable question to ask. Let’s take a closer look at the condition itself, the types of benefits that may be available, and what is necessary to qualify for those benefits.
What Is Diabetes?
Officially known as Diabetes Mellitus – but more commonly simply called “diabetes” – this condition is an endocrine disorder that alters the way the body processes blood sugar. Generally, those with diabetes do not have enough insulin to regulate their blood sugar properly.
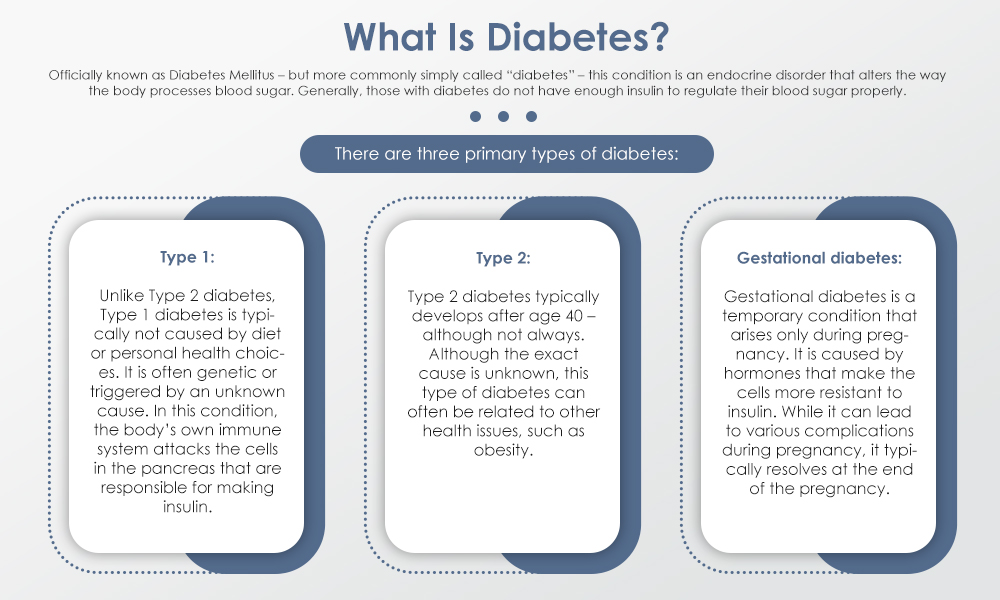
There are three primary types of diabetes:
- Type 1: Unlike Type 2 diabetes, Type 1 diabetes is typically not caused by diet or personal health choices. It is often genetic or triggered by an unknown cause. In this condition, the body’s own immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that are responsible for making insulin.
- Type 2: Type 2 diabetes typically develops after age 40 – although not always. Although the exact cause is unknown, this type of diabetes can often be related to other health issues, such as obesity.
- Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that arises only during pregnancy. It is caused by hormones that make the cells more resistant to insulin. While it can lead to various complications during pregnancy, it typically resolves at the end of the pregnancy.
Although they might not have any of the three primary types of diabetes, many individuals are pre-diabetic. This is the name for the stage that occurs prior to a person becoming a Type 2 diabetic. If appropriate measures are taken, and a person carefully watches their diet, exercise, and other related factors, it may resolve and ultimately not lead to full-blown Type 2 diabetes.
If you struggle with any of these conditions, you may qualify for disability benefits, depending upon the severity of the condition and whether or not you meet the other applicable conditions.
What Types Of Disability Benefits Might Be Available?
The Social Security Administration offers two types of disability benefits to individuals, depending upon their circumstances. Those types of benefits include:

- Social Security Disability Insurance: Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits are paid by the Social Security Administration to disabled individuals with a qualifying medical condition that renders them unable to work for one continuous calendar year or more. To receive SSDI benefits, disabled individuals must also have worked a qualifying job for a sufficient length of time, through which they paid a portion of their salary into the Social Security system.
- Supplemental Security Income: Like SSDI benefits, those who receive Supplemental Security Income (SSI) benefits must have a qualifying medical condition that has rendered them disabled for a period of one continuous calendar year or more. Unlike those who receive SSDI benefits, however, those who receive SSI benefits need not have worked at a qualifying job or paid into the Social Security system. Instead, to qualify for receipt of benefits, applicants must have income and resources below a certain threshold established by the Social Security Administration.
The good news for those applying for disability benefits is that the benefits are not typically dependent upon the particular condition in question. Both types of benefits are available for qualifying medical conditions that render an individual disabled for one year or more. The question is – does diabetes fit that definition?
Is Diabetes A Disabling Condition?
In order to determine whether or not a condition is “disabling,” the Social Security Administration will usually consult its “Blue Book.” The Blue Book is a listing of physical and mental impairments that are often considered severe enough to be disabling, and their accompanying symptoms. Diabetes 1 and 2 are both listed in the Blue Book under the category of “endocrine disorders.”
It is important to remember that even if a condition is listed as a disability in the Blue Book, this does not automatically mean that the Social Security Administration will find it disabling. As many who have diabetes probably already know, both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can be well-controlled in many cases with regular insulin intake and appropriate diet – but not always.
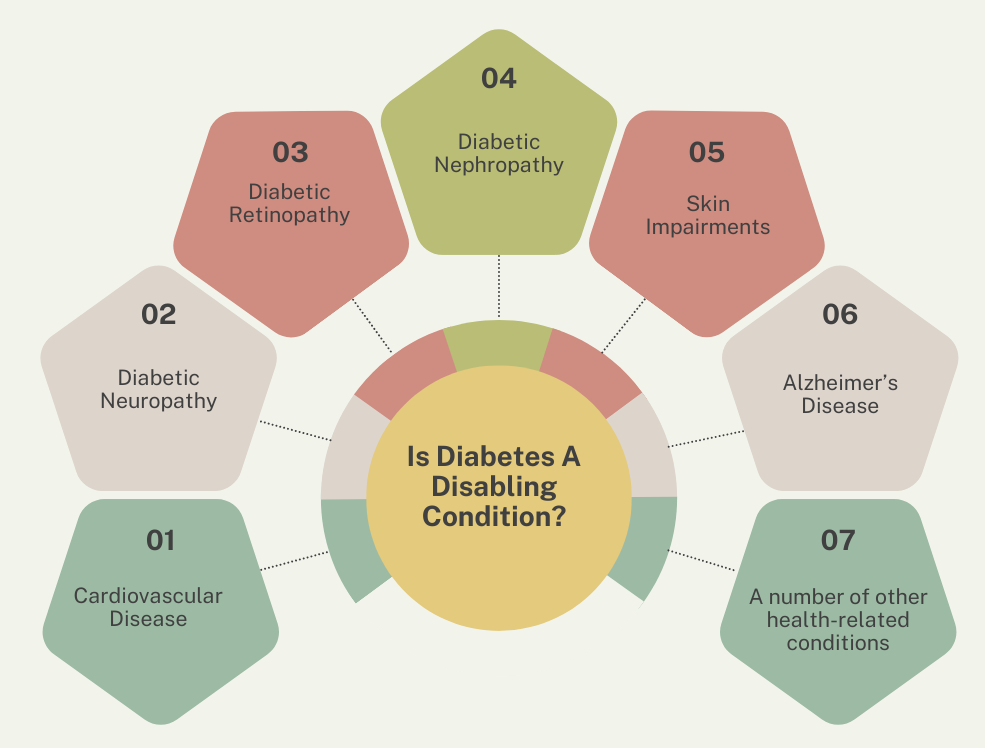
For any number of reasons, an individual may have diabetes that is very difficult to control – or that has led to a related health condition that renders the individual disabled. Some conditions frequently linked to uncontrolled diabetes include:
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetes can significantly increase the risk of many heart problems. Some of these include atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, arrythmias, coronary artery disease, and more.
- Diabetic neuropathy: This is nerve damage caused by diabetes and can lead to a number of health-related difficulties.
- Diabetic retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy is damage to the eyes, which in its most severe form can lead to blindness.
- Diabetic nephropathy: Diabetic nephropathy, or kidney damage caused by diabetes can cause severe health complications.
- Skin impairments: Diabetes can make fighting fungal and bacterial infections more difficult, often leading to skin impairments.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Type 2 Diabetes has been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
- A number of other health-related conditions.
Many of these conditions can ultimately lead to amputations, difficulty seeing and moving, cognitive impairments, depression, and other mental health conditions, and trouble functioning on a day-to-day basis in any number of ways.
For any of these related conditions, the individual seeking benefits must be able to establish, through sufficient medical proof, that they satisfy the specific criteria that are outlined in the Blue Book for that condition. In addition, the applicant must be able to prove that the disability has rendered them unable to work for a full calendar year or more.
How Much Can I Receive In Benefits?
If you are able to establish, through sufficient medical proof, that you have diabetes and a related condition that has rendered you disabled for a period of one calendar year or more, you may qualify for an award of benefits. The next logical and understandable question is, how much might be awarded?
The answer is dependent upon a variety of factors and also depends on whether or not you receive SSDI or SSI benefits. Regardless of which type of benefit you receive, it is important to remember that the amount of benefits will not depend upon your particular condition. Instead, it is dependent upon a variety of other factors and circumstances.
- SSDI Benefits: The Social Security Administration uses a formula to determine how much you will receive in monthly SSDI benefits. SSDI payments usually average around $1,358 per month. The monthly SSDI that an individual will receive is not dependent upon the particular medical condition an individual has. Instead, it is determined based on your lifetime earnings and the amount you paid into the Social Security System. Your payment will typically be based on your average earnings over several years, a figure known as Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME). While this may seem complicated, it can be helpful to use the Social Security Administration’s online benefits calculator to get a general idea of how much you may receive in benefits. In 2023, the maximum SSDI payment is $3,627 a month.
- SSI Benefits: As previously noted, SSI benefits are for individuals who are no to very low-income. In order to qualify for receipt of benefits, an individual must have less than $2,000 in assets, and a married couple must have less than $3,000 in assets. In 2023, the maximum amount of available SSI benefits is $914 for an individual, $1,371 for a married couple, and $458 for an essential person.
Ultimately, the amount that you will receive will be dependent upon your individual circumstances. Like most legal matters, the process of seeking disability benefits can be complex. For that reason, you need a trusted guide you can rely on to help you through the process and ensure that you fully assert your rights.
Clauson Law – Your Disability Benefits Team
At Clauson Law, we are proud to have years of experience fighting for clients just like you – clients who need and deserve benefits as a result of their disability. We understand how essential that financial support can be, and what a difference it can make. That’s why we’ll consistently implement the best legal strategies on your behalf as you pursue your claim. We know and understand the law, and we’re passionate about helping our clients each and every step of the way. If you’re ready to get started, give us a call today. We look forward to speaking with you soon.


